Our ServicesCervical Spine Fractures & Dislocations
- Cervical Fracture: A break in the neck vertebrae.
- Cervical Dislocation: Ligament injury leading to abnormal separation between spine bones.
- Prevalence: ~25,000 cervical fractures annually in the U.S. (Lasfargues, 1995); account for ~50% of spinal injuries.
- High-Risk Scenarios: Motor vehicle accidents, falls, sports, violence.
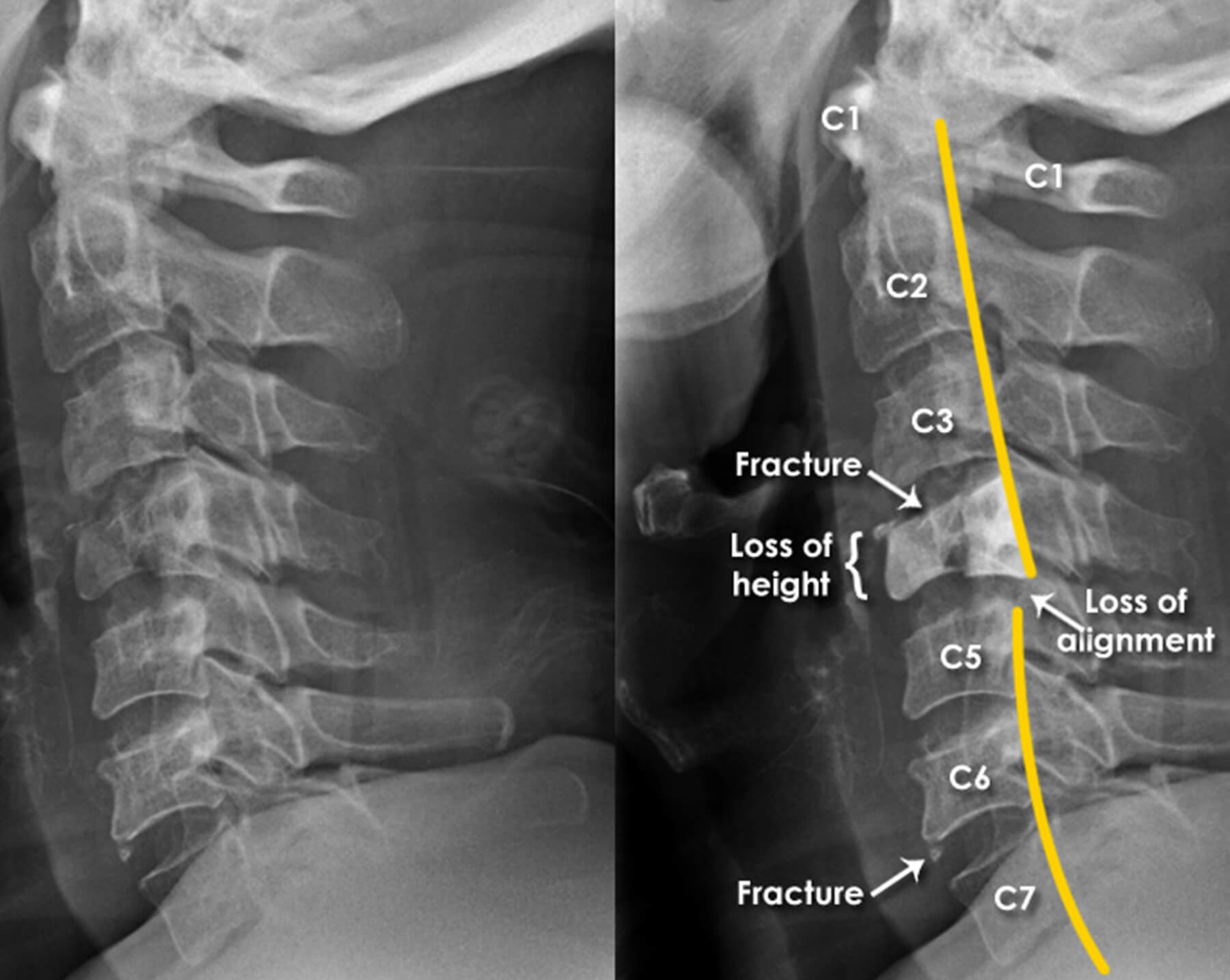
Classification
1. Occipital-Cervical Injuries (Occiput–C2)
- Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation (AOD)
- Occipital Condyle Fracture
- Atlanto-Axial Instability/Rotatory Subluxation
- C1 (Atlas) Fractures
- C2 (Axis) Injuries:
- Odontoid fractures
- Traumatic spondylolisthesis
- Axis body fractures
2. Subaxial Cervical Spine Injuries (C3–C7)
- Injury types based on mechanism:
- Distraction-Flexion (DF)
- Vertical Compression (VC)
- Compression-Flexion (CF)
- Compression-Extension (CE)
- Distraction-Extension (DE)
- Lateral Flexion (LF)
Back pain and beyondWhen conservative
When conservative  care needs
care needs
a specialist’s touch.
touch.
Physical Examination
Local tenderness, spasm, swelling
Limited range of motion
Step-off deformity
Neurologic deficits if spinal cord is compromised
Imaging & Diagnosis
X-Ray: Initial imaging
CT Scan: Gold standard for bony detail
MRI: Best for soft tissue, spinal cord, and ligament evaluation
Flexion/Extension Views: Assess ligamentous instability
Labs: Not typically diagnostic
Treatment Overview
01.
Goals:
- Preserve/improve neurologic function
- Stabilize the spine
- Alleviate pain
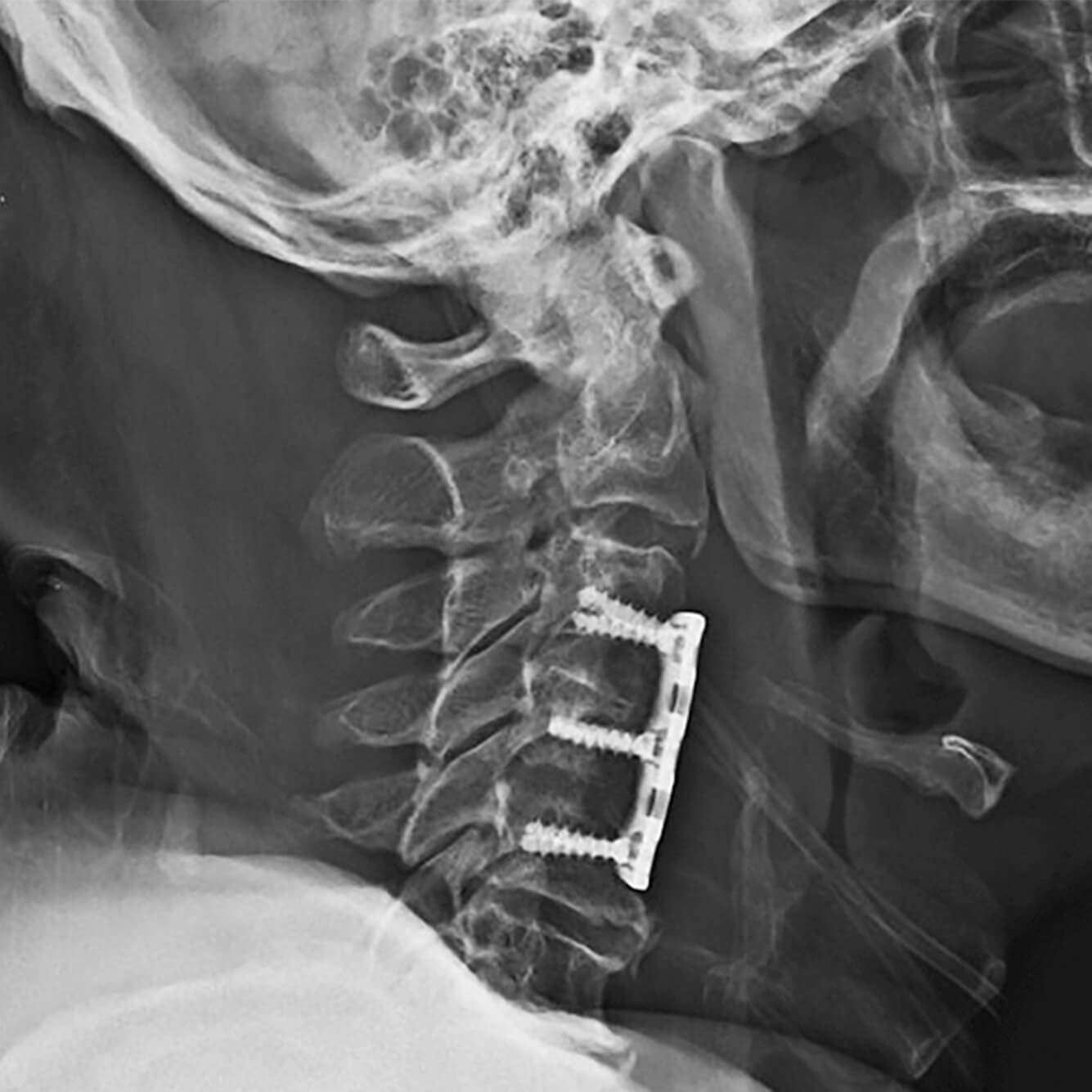
Cervical Spine Fractures & DislocationsTreatment Guidelines by Injury Type
Occipital-Cervical Injuries
- AOD: Almost all need Occ-C2 posterior spinal fusion (PSF) after halo vest reduction.
- Occipital Condyle Fx:
- Type I/II: CT orthosis 6–8 weeks
- Type III (stable): Cervical orthosis
- Type III (unstable): Occ-C2 PSF
- Atlanto-Axial Instability:
- TAL rupture >5 mm: Surgery
- C1 fx with >7 mm displacement: Halo → C1-C2 PSF
Rotatory Subluxation: Halo traction → Surgery if pain/deformity persists
Atlas Fx (C1): Mostly non-operative unless >7 mm displacement
Axis (C2) Fractures
- Odontoid Fx:
- Type I: Orthosis
- Type II: <5 mm displ – Halo; >5 mm – Reduction + Fusion/Screw fixation
- Type III: Similar to Type II
- Spondylolisthesis (Hangman’s fracture):
- Type I: Orthosis
- Type II/IIA: Halo → Possible surgery
- Type III: Surgery (ACDF + PCF if needed)
Subaxial Injuries (C3–C7)
- DF (Facet dislocation): Closed reduction → PCF; ACDF + PCF if needed
- CF: Stable – Orthosis; Unstable – ACVF ± PCF
- VC: Stable – Orthosis; Unstable – ACVF
- CE/DE: Check for disc injury → ACDF if unstable
- LF: ACDF