Our ServicesThoracic Spine Fractures and Dislocations
The thoracic spine-the middle segment of the vertebral column-plays a critical role in supporting the upper body and protecting the spinal cord. Although less common than cervical or lumbar injuries, thoracic spine fractures and dislocations are serious conditions that can result in significant pain, disability, and even paralysis if not treated promptly.
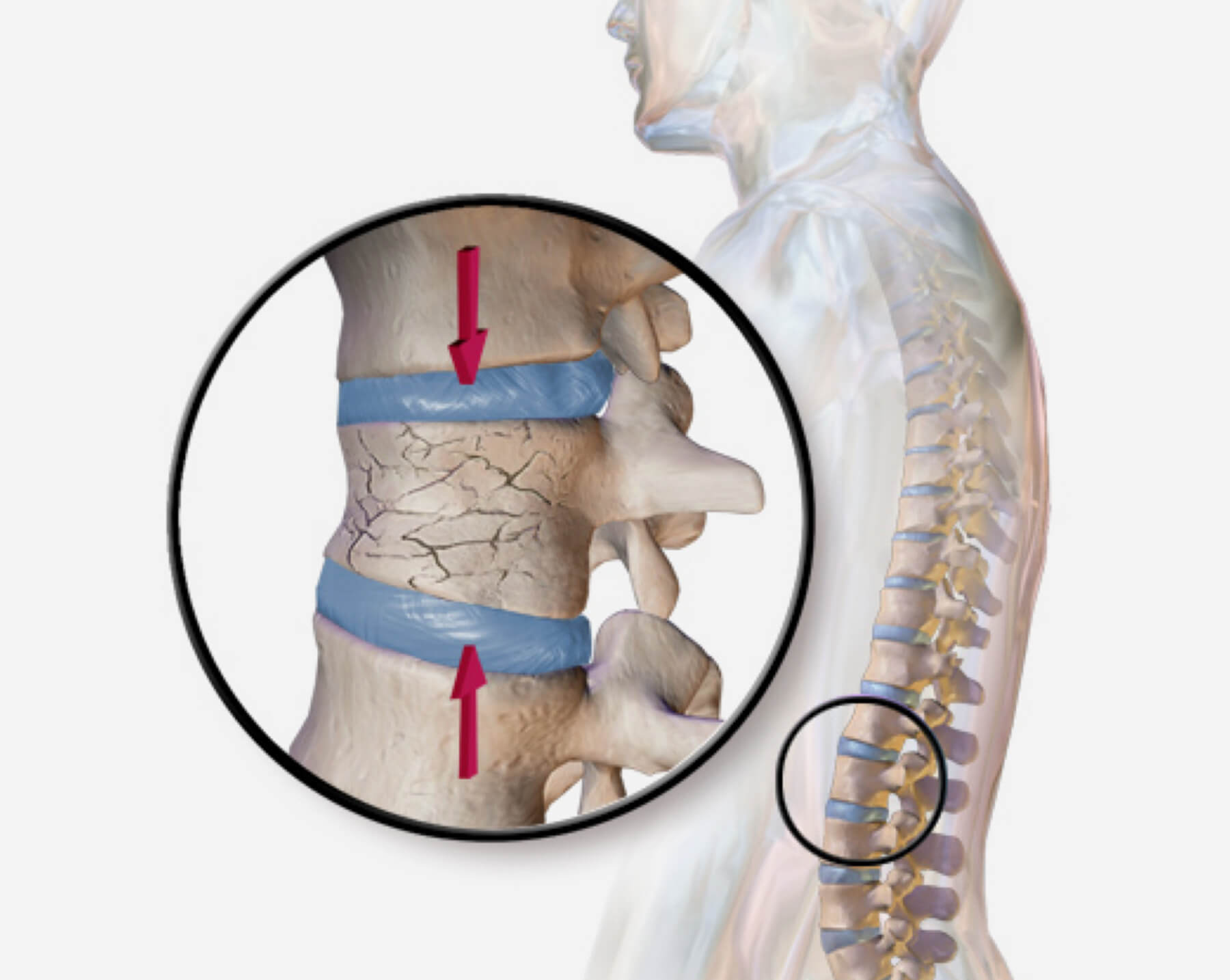
What Is the Thoracic Spine?
The thoracic spine comprises 12 vertebrae (T1–T12) located between the cervical spine (neck) and the lumbar spine (lower back). These vertebrae are connected to the rib cage, providing extra stability but also making the area more vulnerable to high-impact trauma.
When conservative  care needs
care needs
a specialist’s touch.
touch.
Causes of Thoracic Spine Fractures and DislocationsThoracic spine injuries are usually the result of high-energy trauma or degenerative changes. Common causes include:
Motor vehicle accidents
Falls from height
Sports injuries
Osteoporosis or metastatic cancer (which can weaken vertebrae)
Violent trauma (e.g., gunshot wounds or assault)
Types of Thoracic Spine Injuries
Compression Fractures: Caused by a sudden downward force that compresses the vertebra.
Burst Fractures: Result when the vertebra is crushed in all directions, possibly sending fragments into the spinal canal.
Flexion-Distraction Injuries: Often seen in car accidents, where the spine is forcefully bent forward.
Fracture-Dislocations: A combination of fracture and dislocation, often resulting in spinal instability.
SymptomsThe severity of symptoms depends on the nature and extent of the injury. Common symptoms include:
Intense back pain, especially at the site of the injury
Numbness or tingling
Weakness in the limbs
Loss of bladder or bowel control (in severe cases)
Visible deformity or swelling
Difficulty walking or standing
DiagnosisA thorough clinical examination followed by imaging studies is essential. Diagnostic tools include:
X-rays: To detect fractures or misalignment
CT scans: Provide a detailed image of bone damage
MRI: Helpful in evaluating spinal cord involvement and soft tissue injury
Treatment Options
01.
Non-Surgical Treatment
- Bracing: For stable fractures without neurological symptoms.
- Pain management: Includes NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, or epidural injections.
- Physical therapy: Helps restore mobility and strength.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery depends on the severity of the injury and the treatment used. Most patients require physical therapy for several months to regain mobility and strength. Early intervention and a comprehensive rehab program are key to improving outcomes.
Prevention Tips
Use seat belts and follow traffic safety
Install safety measures in homes, especially for the elderly
Manage osteoporosis with medication and calcium/vitamin D supplements
Use proper techniques when lifting or engaging in sports
Final Thoughts
Thoracic spine fractures and dislocations are serious injuries that require immediate medical attention. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment-whether conservative or surgical-patients can often return to a functional life. If you or someone you know experiences severe back pain after trauma, seek medical evaluation without delay.