Our ServicesKyphoscoliotic Deformity
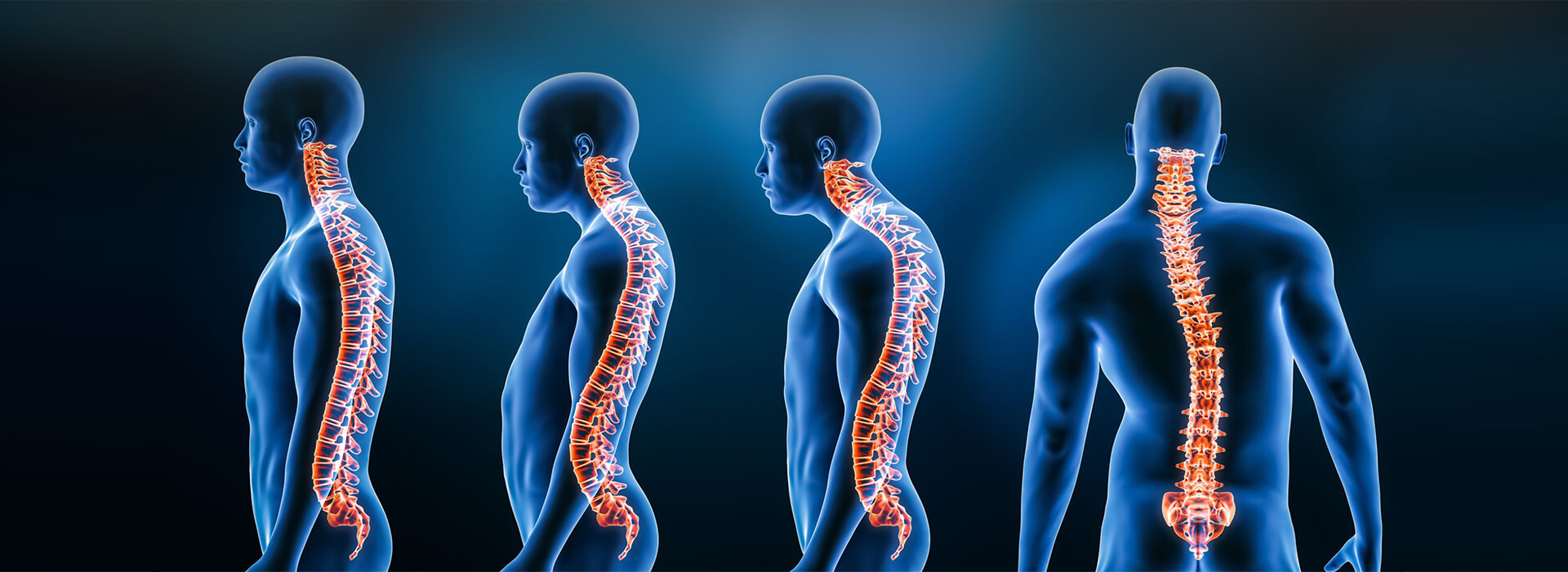
Spinal health plays a crucial role in overall well-being, mobility, and posture. Among the many spinal deformities, kyphoscoliotic deformity is a complex and relatively rare condition that combines features of both kyphosis and scoliosis. If left untreated, it can lead to significant complications, including breathing difficulties and reduced quality of life.
What is Kyphoscoliotic Deformity?
Kyphoscoliosis is a spinal disorder characterized by an abnormal curvature in both the coronal (side-to-side) and sagittal (front-to-back) planes of the spine. In simpler terms, it involves:
- Kyphosis: An exaggerated forward rounding of the upper back (commonly referred to as a hunchback).
- Scoliosis: A sideways curvature of the spine.
When these two curvatures coexist, the spine becomes twisted and hunched, leading to a visibly abnormal posture and potential complications.
When conservative  care needs
care needs
a specialist’s touch.
touch.
Causes of KyphoscoliosisKyphoscoliotic deformity may be congenital, idiopathic, or acquired:
Congenital: Caused by vertebral malformations present at birth.
Neuromuscular: Linked to conditions like cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or spinal muscular atrophy.
Idiopathic: No identifiable cause, often seen in adolescents.
Postural or Degenerative: Due to poor posture, aging, or spinal degeneration.
Infectious or Inflammatory: From diseases like tuberculosis (Pott’s disease) or ankylosing spondylitis.
Traumatic: Resulting from injury or spinal fractures.
Symptoms and Clinical FeaturesThe severity of symptoms depends on the degree of curvature and the underlying cause. Common signs include:
Visible hunching or sideways bending of the back
Uneven shoulders or hips
Limited spinal flexibility
Chronic back pain
Fatigue due to muscle strain
Breathing difficulty due to compression of the chest cavity
Neurological symptoms in severe cases (numbness, weakness)
DiagnosisEarly diagnosis is key to effective management. Diagnosis typically includes:
Physical examination to assess spinal alignment
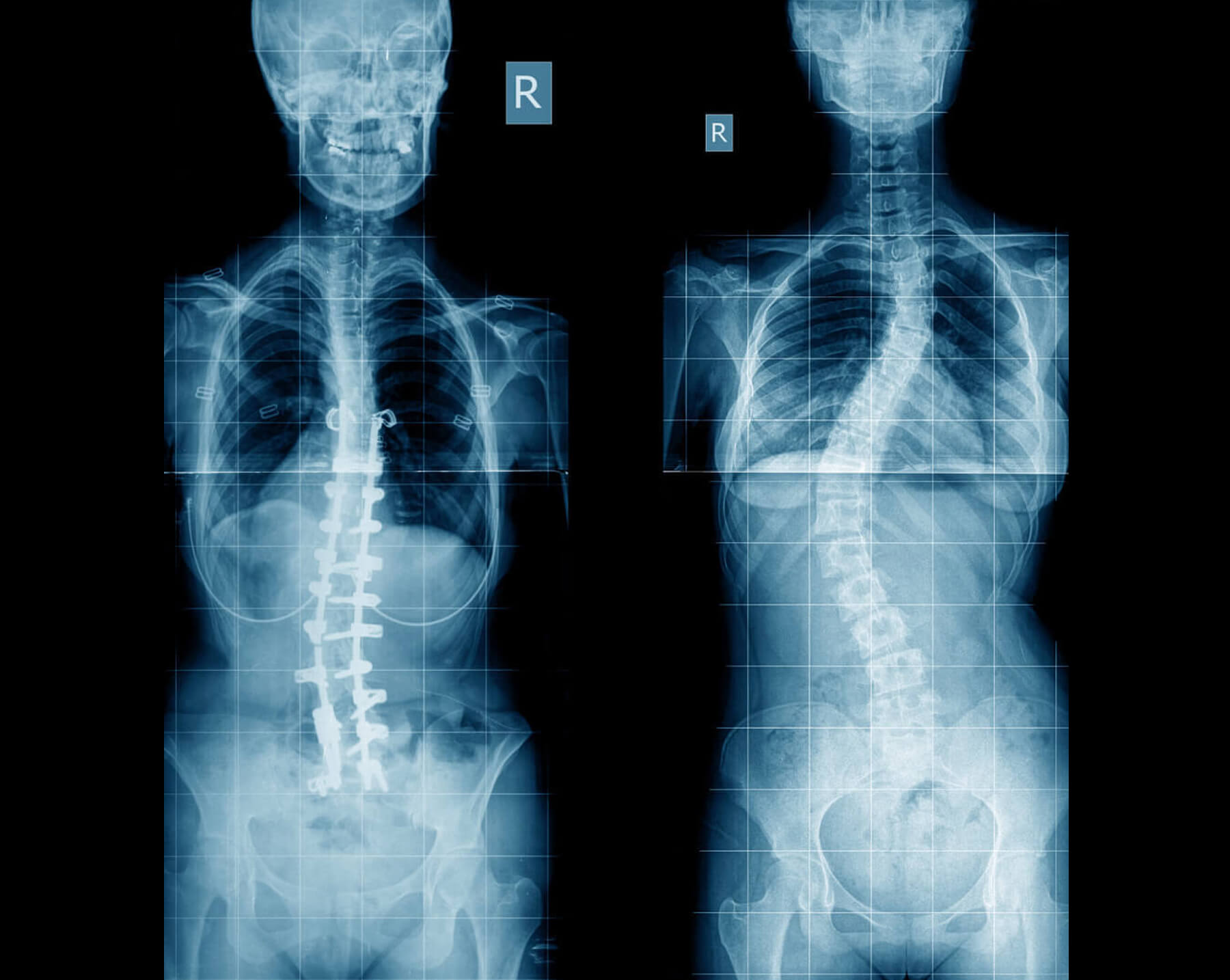
X-rays and MRI/CT scans to determine the degree and structure of curvature
Pulmonary function tests if respiratory compromise is suspected
Neurological evaluations in case of nerve involvement
Treatment Options
The goal of treatment is to prevent progression, relieve symptoms, and improve function. Treatment plans vary based on age, severity, and underlying causes:01.
Non-Surgical Management
- Bracing: Used in growing children or adolescents to halt progression
- Physical therapy: Improves posture, strengthens muscles, and enhances flexibility
- Pain management: Medications or physical modalities for relief
- Respiratory therapy: For patients with reduced lung function
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is considered in severe cases, especially when:
- The curvature is progressive and >50–60 degrees
- There is significant respiratory or neurological compromise
- Conservative measures fail
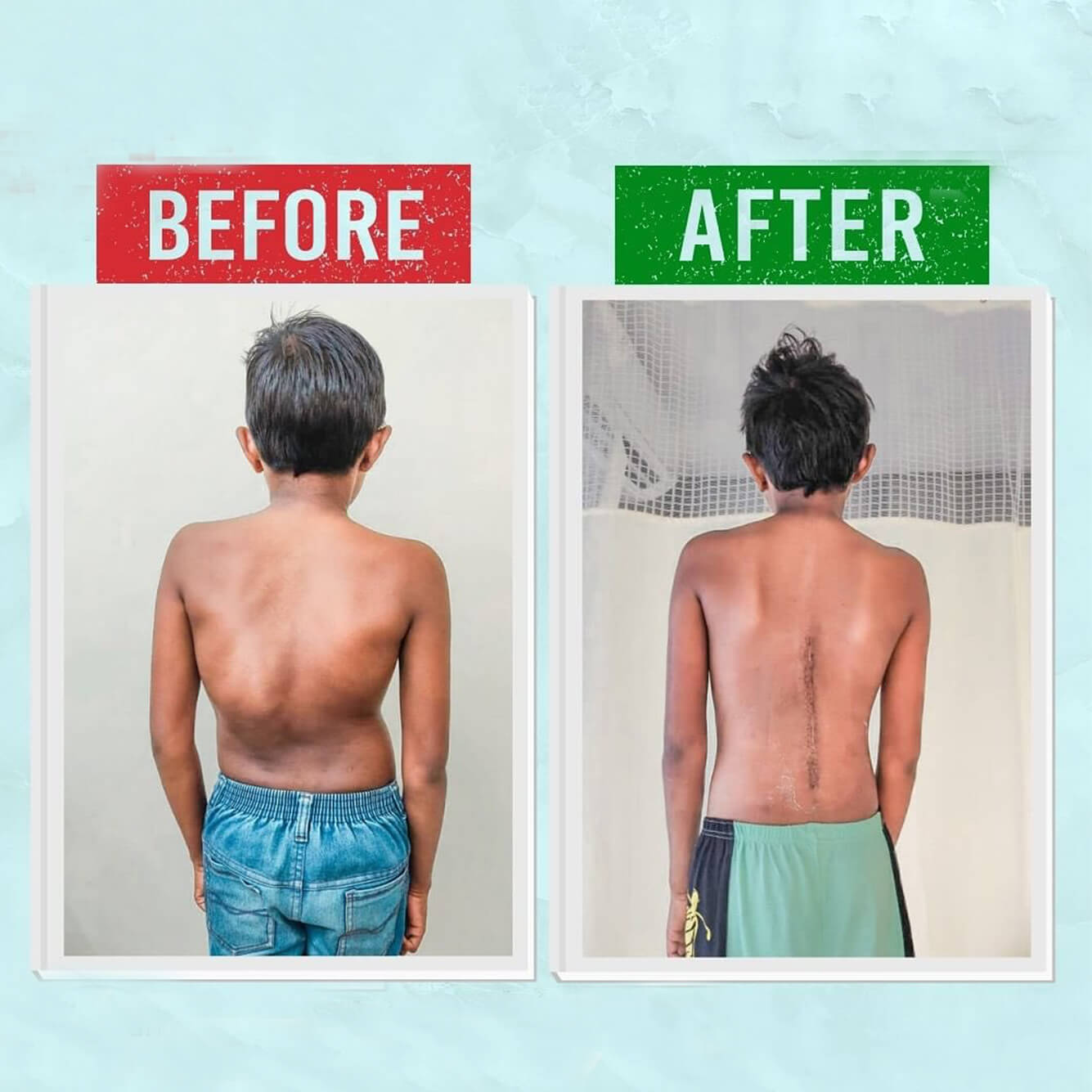
Spinal fusion and instrumentation are common surgical procedures to correct and stabilize the spine.
Living with Kyphoscoliosis
Patients with mild deformities can often lead normal lives with proper medical care and lifestyle adaptations. Regular follow-up, exercise, and posture correction go a long way in managing the condition.
For more severe forms, especially those diagnosed early, timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes, including physical appearance, lung capacity, and overall quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Kyphoscoliotic deformity is more than just a postural issue—it can be a progressive condition with systemic implications if ignored. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare provider, understanding the condition is the first step toward effective management.
If you or a loved one is showing signs of spinal curvature, consult an orthopedic or spine specialist for a detailed evaluation. Early action can make all the difference.