Our ServicesFacet Fractures
When we think of spinal injuries, we often hear about herniated discs or vertebral fractures—but one lesser-known, yet important, spinal injury is the facet fracture. This condition affects a crucial part of the spine called the facet joint, which plays a vital role in stabilizing the spinal column and enabling movement.
In this blog, we’ll break down what facet fractures are, how they occur, their symptoms, and how they can be treated.
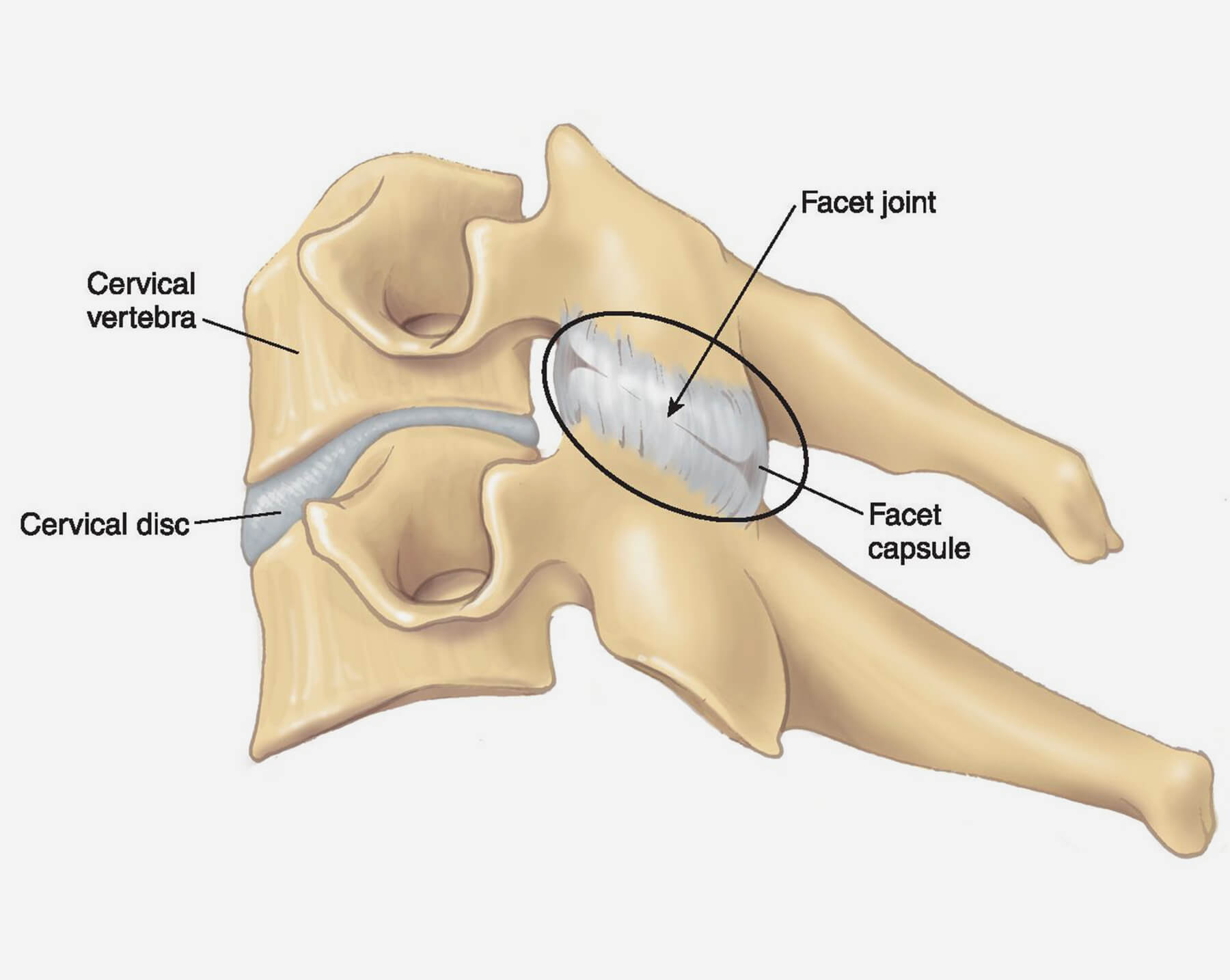
What Are Facet Joints?
Facet joints are small, paired joints located at the back of the spine, connecting each vertebra to the one above and below. These joints help guide and limit the movement of the spine, preventing excessive twisting or bending. Each vertebra has two facet joints—one on each side.
When one or more of these joints fracture, it can lead to pain, limited mobility, and potential instability in the spine.
When conservative  care needs
care needs
a specialist’s touch.
touch.
What is a Facet Fracture?
A facet fracture refers to a break or crack in one of the facet joints. It can happen on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral), and is often associated with high-impact trauma or spinal injuries.
Facet fractures most commonly occur in the cervical spine (neck region), although they can also affect the thoracic (mid-back) or lumbar (lower back) areas.
Causes of Facet FracturesFacet fractures usually result from high-energy trauma, such as:
Car or motorcycle accidents
Falls from a height
Sports injuries, especially in contact sports
Violent twisting or hyperextension of the spine
Sometimes, facet fractures are associated with other spinal injuries like vertebral fractures, disc herniation, or spinal cord compression.
Symptoms of a Facet FractureThe symptoms depend on the location and severity of the fracture, but may include:
Localized pain at the site of the fracture
Stiffness or reduced range of motion
Muscle spasms
Numbness or tingling (if nerves are affected)
Radiating pain in the arms or legs
Weakness or paralysis in severe cases involving nerve damage in the arms or legs
If the spinal cord is involved, it may lead to more serious neurological symptoms and requires immediate medical attention.
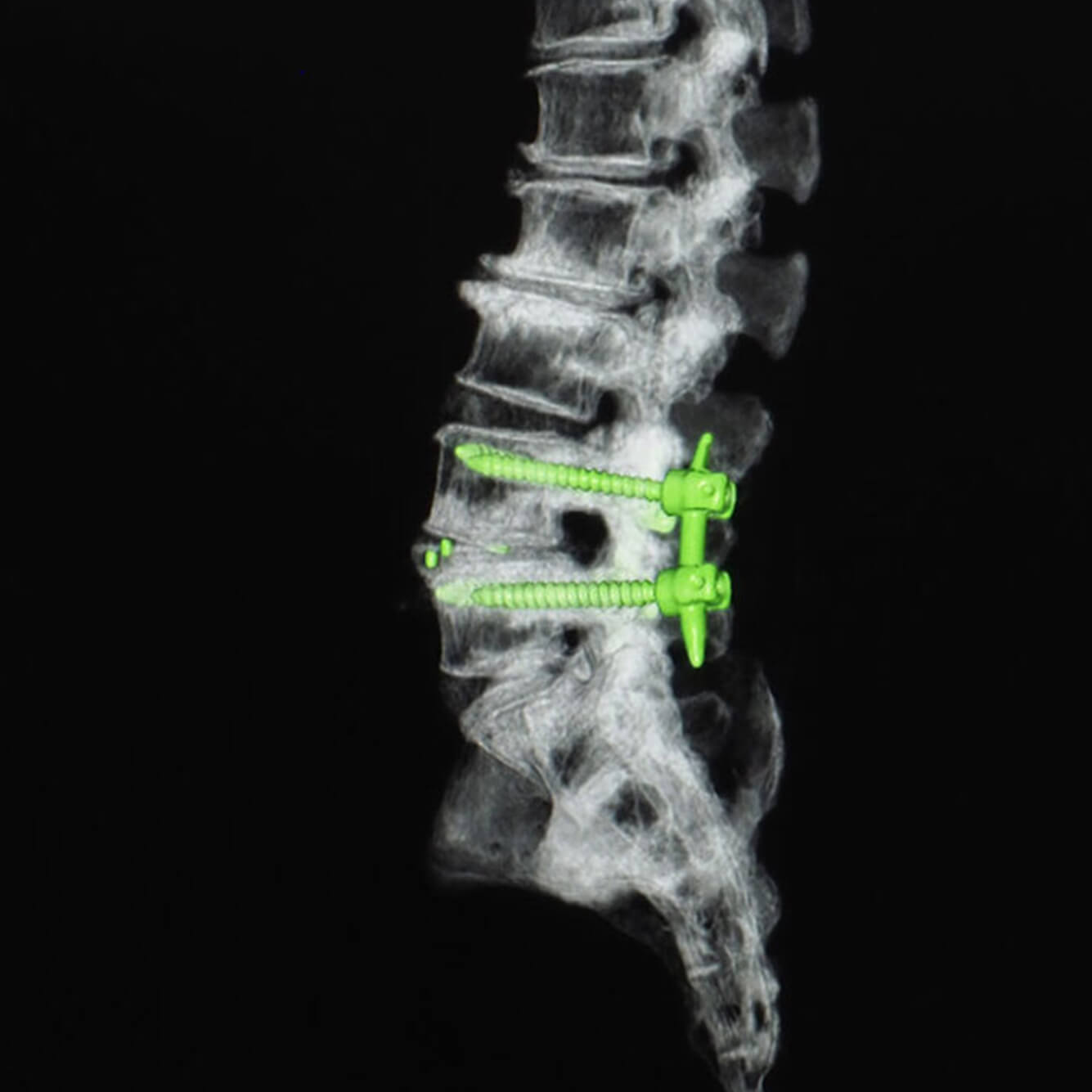
Treatment Options
The treatment plan depends on the severity of the fracture and whether the spine is stable.
- Non-Surgical Treatment
- Rest and bracing to immobilize the spine
- Pain management with medications
- Physical therapy to restore mobility and strength once healing begins
- Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be necessary if:
- The fracture is unstable
- There is nerve or spinal cord compression
- There is severe pain that doesn’t respond to conservative measures
Surgical procedures might include:
- Spinal fusion to stabilize the affected vertebrae
- Decompression surgery to relieve pressure on nerves
- Instrumentation (rods, screws) to support the spine during healing
This approach is usually recommended for stable, non-displaced fractures.
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery from a facet fracture varies based on the injury and treatment approach. Most people recover fully with proper care, though severe injuries may require long-term rehabilitation.
With physical therapy and gradual return to activity, many patients can regain normal function and live pain-free.
Prevention TipsWhile accidents are unpredictable, you can reduce the risk of spinal injuries by:
Wearing seat belts while driving
Using proper technique during sports and workouts
Strengthening core muscles to support spinal health
Avoiding high-risk activities without proper training or safety gear
Final Thoughts
Facet fractures, though less common than other spinal injuries, can have significant impacts on mobility and quality of life. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for a good recovery.
If you or someone you know experiences sudden back or neck pain after trauma, don't ignore it—consult a medical professional immediately.